Bioacoustic approaches for ecosystem monitoring and conservation
Background
Protecting biodiversity requires continuous, scalable, low-cost monitoring, and this project focuses
specifically on birds. Acoustic sensors such as AudioMoth (a low-cost acoustic recorder) provide
non-invasive, wide-coverage recordings that convert bird sounds into usable ecological data. We distill
Google’s Perch Bird Vocalization Classifier into a compact, quantized, edge-ready student model using
Perch-based knowledge (teacher logits only — the teacher’s probability outputs).
The student is
pretrained on diverse public recordings (Xeno-Canto) and then fine-tuned on DSAIL’s field dataset (300+
hours of AudioMoth recordings, ~20 hours hand-annotated across ~80 bird species) to optimize for local
species, signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), and recorder acoustics. The resulting model will run on low-cost
recorders and microcontrollers (AudioMoth, Raspberry Pi Pico, tinyRANGER) and stream detections to the
DSAIL dashboard for telemetry and human validation. This enables timely, scalable bird monitoring to
inform conservation actions, detect range shifts or invasions early, and support community science.
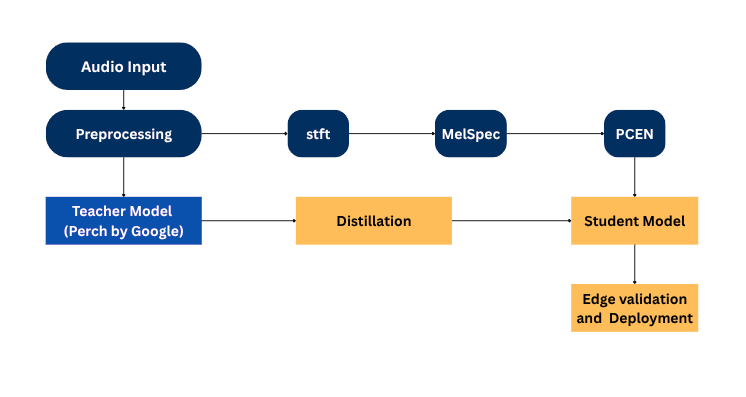
Technical Implementation
- Pipeline Verification: Implemented a preprocessing pipeline (STFT → Mel Spectrogram
→ PCEN) ensuring student inputs match the teacher model.
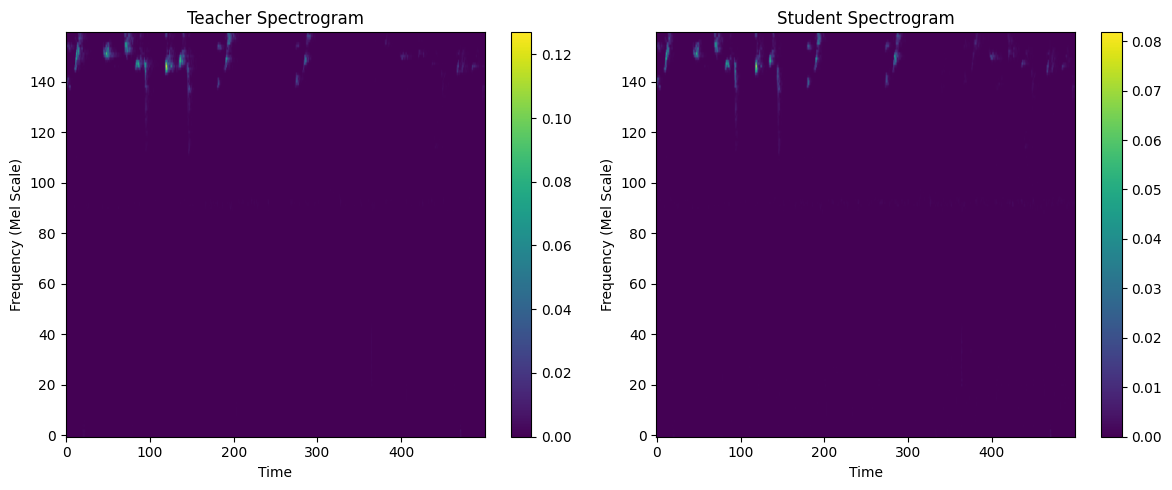
- Quality Assurance: Analyzed spectrogram alignment between teacher and student to
guarantee high-fidelity input features.
Next Steps
- Implement Student Model: Develop and train a lightweight student network capable of learning from the teacher’s intermediate representations and/or final logits.
- Quantization & Edge Optimization: Apply model compression and quantization techniques to ensure deployment feasibility on resource-constrained hardware.
- Evaluation & Benchmarking: Compare teacher vs. student performance on accuracy, inference speed, and power efficiency.
- Field Testing & Deployment: Integrate the optimized model into edge devices for real-world birdcall detection and performance validation.
- Documentation & Publication:Consolidate findings into a research paper or technical report detailing the methodology, results, and open challenges in distillation for bioacoustics.